Renewables Are Key to Zero Waste in Fashion and Textiles
March 30, 2025
This International Day of Zero Waste: towards zero waste in fashion and textiles, we invited our Nabilah Tarin, Strategic Communications Expert at REN21, to publish a guest blog on how renewable energy can help us conserve resources, and reduce waste in the fashion and textile industry. Read on to find out!
Managing the waste crisis is key to addressing climate change. With billions of tons of waste produced annually, the environmental and social consequences are severe: the production, distribution, and disposal of products generate greenhouse gases, pollute ecosystems, and threaten human health.
The fashion industry is a major contributor, responsible for around 10% of global carbon emissions and 20% of global wastewater. It also generates 92 million tonnes of textile waste annually—equivalent to a rubbish truck of clothes dumped every second. Producing one cotton T-shirt requires 2,700 litres of water, enough for one person’s drinking needs for 2.5 years.
Fast fashion, or clothes made from plastic materials like spandex, polyester, nylon, acrylic, and vegan ‘leather’ worsens the issue, releasing microplastics into the oceans and pollution from garment factories harming local communities and ecosystems. In fact, 60% of our clothing these days is fast fashion, made from dirty fossil fuels.
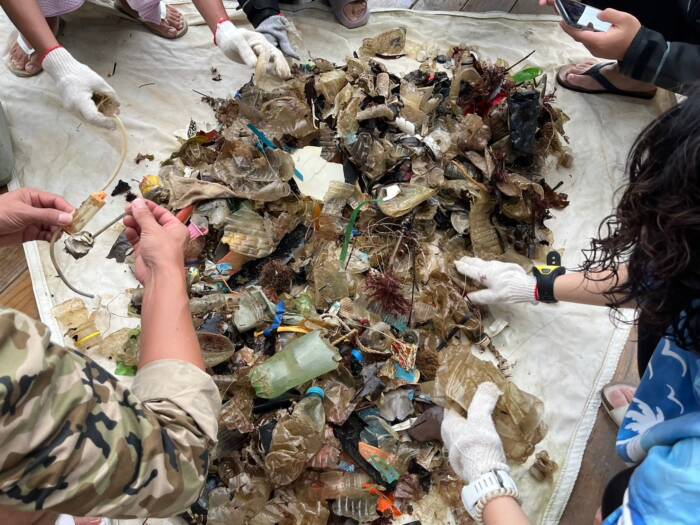

Volunteer divers and students in Taiwan collected 10.83 kilograms of waste in one just day, which included plastic debris, metal scraps, and even discarded tires, during 350’s Power Up! mobilization in 2023.
However, there are solutions to this crisis. Integrating renewable energy into industries, supply chains, and waste management systems—alongside embracing circular fashion and sustainable practices—can significantly reduce this waste.
Renewables can reduce energy consumption during production
The fashion and textile industries are among the highest energy consumers, often powered by dirty fossil fuels. Clothing production is a major contributor to global carbon emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can significantly lower factories’ carbon footprints, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing environmental impact. Collaborative efforts such as introducing sustainable and circular textile models can drive clean energy adoption, making production more sustainable while cutting waste.

Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can significantly lower factories’ carbon footprints
A zero-waste future is about longevity and rethinking product life cycles. For example, instead of fast fashion clothing, we need to turn to longer-lasting fabrics and textiles coming from durable, repairable, reusable and recyclable materials. Furthermore, the misinformation about textiles must be addressed, shining a light on the real impacts of mass consumption and fast fashion have on both nature and people.
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in this shift. Textile recycling, which relies on energy-intensive processes, becomes more sustainable when powered by clean energy. Integrating solar and wind energy into recycling operations ensures that the entire lifecycle—from production to disposal—aligns with circular economy principles. Circular economy strives to eliminate waste and reduce pollution, extend the life of products and regenerate natural systems. For example, the European Union has introduced an Ecolabel and the Green Deal that aims to give more visibility to less energy-consuming and eco friendly production line products. This approach helps close the loop through efficient, low-carbon recycling processes.
It’s important to keep in mind though that while any clothing made from recycled materials like plastic bottles may seem eco-friendly, it doesn’t always reduce plastic production and often such items can’t be recycled again, contributing to more waste. Many brands promote such items as 100% sustainable, but this is misleading, as they often contain minimal recycled content.
Renewables provide better waste management solutions
Renewable energy also enables innovative waste management solutions. Technologies like anaerobic digestion and waste incineration convert waste into bioenergy, reducing landfill waste while generating clean energy. These waste-to-energy processes are particularly important for non-recyclable materials, such as textile waste, that contribute to pollution. Transforming waste into valuable resources helps reduce environmental harm.
How can businesses and governments use renewable energy to produce less waste?
Businesses must commit to creating products that are durable, repairable, reusable, and recyclable or what is known as circular product design along with renewable energy solutions to embrace a zero-waste model. Prioritizing renewable energy reduces companies’ carbon footprints and supports waste reduction efforts. Renewable-powered circular business models are already proving successful, allowing companies to produce goods with minimal waste.
Governments also play a crucial role in accelerating the transition to renewable energy and zero waste. Enacting policies to encourage circular practices, and incentives for renewable energy adoption help sustain these efforts. For instance, Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy that holds producers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including post-consumer disposal and recycling, encouraging sustainable product design and waste reduction. With global renewable energy capacity increasing by 54% in 2023, such shifts are increasingly viable.
Let’s make renewables fashionable!
The potential of renewable energy to drive zero-waste initiatives is immense. Investment in renewable technologies grew by 70% in 2023, reflecting a global shift toward sustainability. As industries integrate renewable solutions, they reduce carbon footprints while contributing to a circular economy that minimizes waste across production and consumption.
By embedding renewable energy into waste management and textiles, we move toward a sustainable, zero-waste future—one that protects the planet while fostering economic growth, employment, and resilience against environmental challenges.
Key Data at a Glance:
- Renewable Energy Capacity Growth: Increased by 54% in 2023, reaching 4,034 GW.
- Investment in Renewable Technologies: Grew by 70% in 2023, reaching USD 200 billion.
- Employment in Renewables: Rose by 8% in 2022, with 13.7 million jobs globally.
These developments highlight the exciting potential of renewable energy in achieving zero-waste objectives, which can help us fight the climate crisis and ensure a cleaner, greener future for generations to come.
Click here fora deeper understanding of renewables in industry. Learn more about the benefits of renewables at ren21.net
Search
RECENT PRESS RELEASES
Related Post